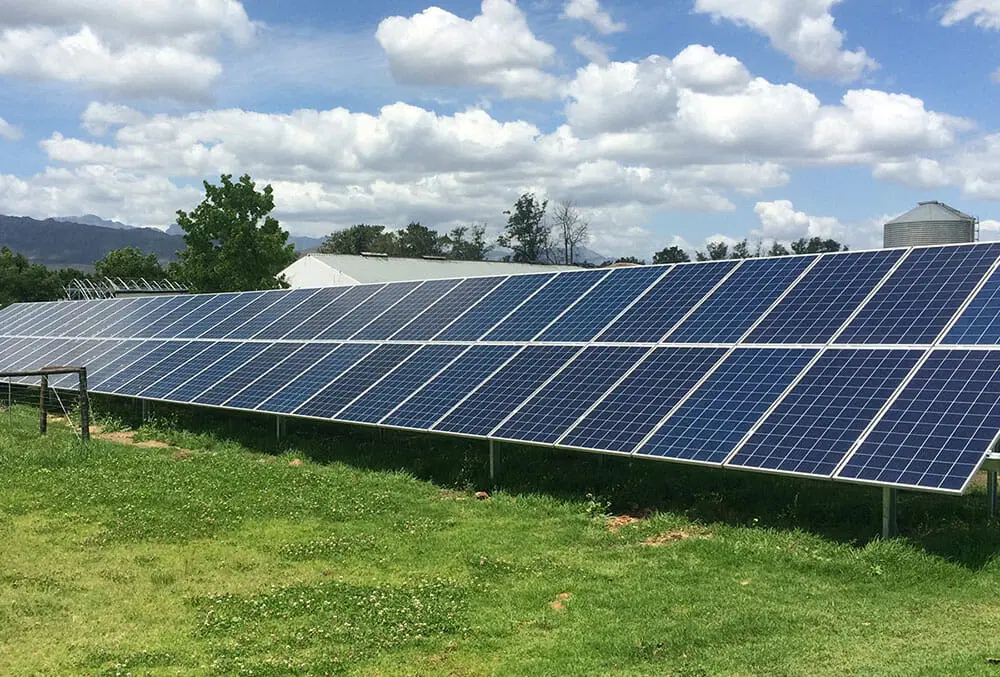

As the demand for renewable energy solutions grows, solar structure construction has become a crucial part of harnessing solar power efficiently. Properly designed and constructed solar structures provide long-term stability, durability, and optimal energy generation. Whether for borehole solar pumping systems, residential rooftops, or large-scale solar farms, having a strong solar mounting structure is essential for efficiency and safety.
At River Best Kenya, we specialize in customized borehole solar structure construction, ensuring reliable installations that withstand harsh weather conditions while maximizing solar energy absorption.
Importance of Solar Structure Construction
A well-built solar panel structure is essential for ensuring maximum sunlight exposure, maintaining structural integrity, and enhancing longevity. A carefully designed solar mounting system optimizes the angle and positioning of solar panels, allowing them to capture and convert sunlight efficiently. Without a stable foundation, solar panels may experience inefficiencies, structural failures, or frequent maintenance issues.
Investing in high-quality solar structures minimizes the risk of panel damage due to wind, rain, or external pressure. It also reduces maintenance costs by providing long-term durability and stability. Proper materials like galvanized steel, aluminum frames, and concrete foundations contribute to a strong structure that can withstand environmental factors.
Key Benefits of Proper Solar Structure Construction:
- Enhanced Energy Efficiency: Optimized angles and placement increase solar energy capture.
- Structural Durability: Sturdy materials prevent damage from wind, rain, and external forces.
- Reduced Maintenance Costs: Strong foundations reduce wear and tear on solar panels.
- Scalability: Allows for future expansion of solar systems with minimal structural modifications.
Types of Solar Structures
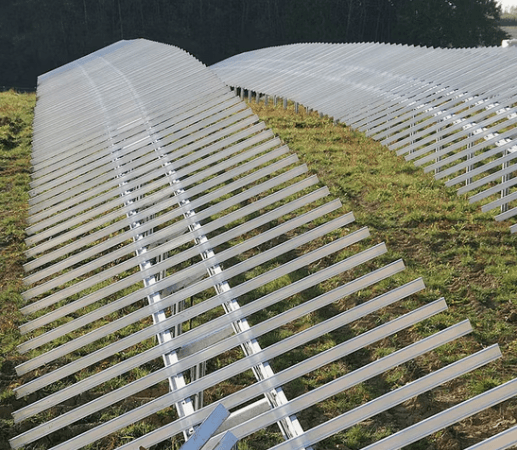

1. Ground-Mounted Solar Structures
These structures support solar panels on the ground and are common in large-scale solar farms, commercial spaces, and off-grid borehole systems. They are ideal for areas with ample space and require proper alignment to maximize sunlight exposure.
2. Roof-Mounted Solar Structures
Installed on residential, commercial, or industrial rooftops, these structures save space while utilizing existing infrastructure. They require a strong roof foundation and proper mounting to withstand weather changes.
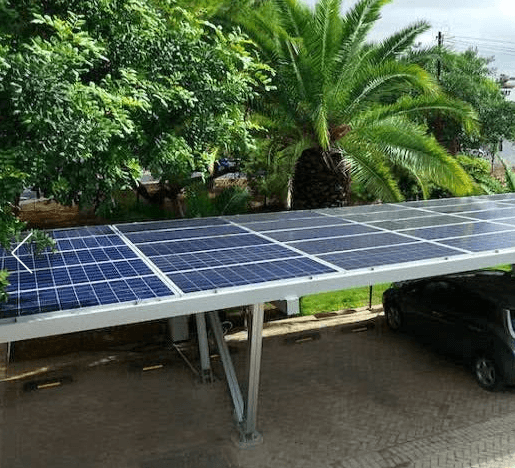
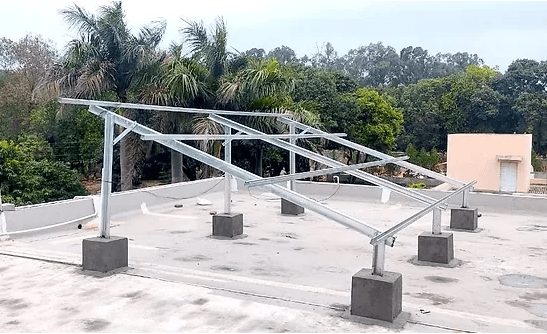

3. Solar Carport Structures
Solar carports provide shade for vehicles while generating electricity. They are commonly used in homes, offices, and commercial parking lots and contribute to sustainable energy use.
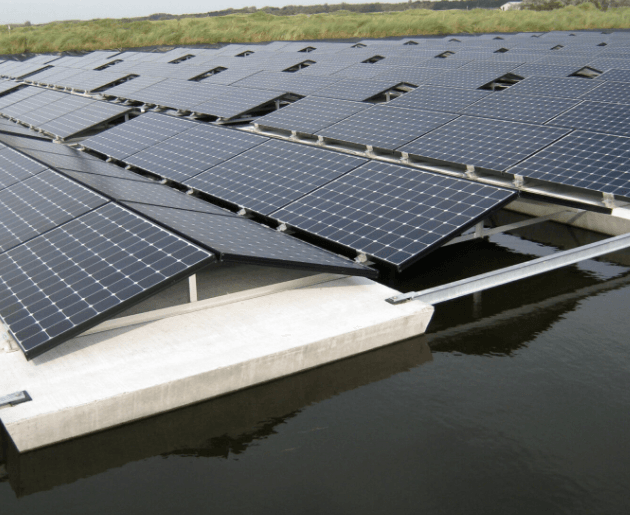
4. Floating Solar Structures
These are innovative solutions where solar panels are mounted on floating platforms on water bodies. They help conserve land and reduce evaporation in dams, reservoirs, and fish ponds.

Steps in Solar Structure Construction
Step 1: Site Assessment and Planning
Before construction, a thorough site analysis is conducted to determine the best location, panel orientation, and structural requirements. Key factors include:
- Sunlight availability and shading analysis
- Soil conditions for ground-mounted structures
- Roof strength for rooftop installations
- Wind and weather considerations
Step 2: Selecting the Right Materials
The durability and performance of solar structures depend on the materials used. Common materials include:
- Galvanized steel – Resistant to rust and corrosion.
- Aluminum frames – Lightweight, strong, and durable.
- Concrete foundations – Provide stability for ground-mounted structures.
Step 3: Structural Design and Fabrication
Based on the site assessment, an engineered solar structure is designed to meet specific load requirements. The fabrication process involves:
- Cutting and welding metal frames
- Assembling the mounting system
- Ensuring proper weight distribution for durability
Step 4: Installation and Mounting of Solar Panels
Once the structure is ready, solar panels are securely mounted at the right angle for maximum sun exposure. Proper alignment and fastening techniques ensure long-term stability.

Factors to Consider in Solar Structure Construction
1. Load Capacity and Wind Resistance
A strong solar mounting structure must withstand high winds, storms, and heavy rainfall. Engineering calculations ensure the structure meets regional weather standards.
2. Tilt Angle and Orientation
The optimal tilt angle and panel direction depend on the geographical location to maximize solar energy absorption.
3. Structural Stability and Corrosion Resistance
Materials should be corrosion-resistant, especially in coastal or humid areas, to prolong the lifespan of solar mounting systems.
4. Accessibility for Maintenance
The structure should allow for easy cleaning and servicing of solar panels without causing physical strain or damage.
Solar Structures for Borehole Pumping Systems
For borehole solar pumping, robust and durable solar mounting structures are essential to effectively support the solar panels and ensure a constant water supply. These well-designed structures play a crucial role in:
- Providing stable energy for pumping systems
- Protecting solar panels from external damage
- Enhancing long-term borehole efficiency
Common Challenges in Solar Structure Construction
1. Poor Site Selection
Installing solar structures in shaded areas significantly reduces their efficiency and overall energy output. Conducting a thorough site assessment beforehand helps prevent this issue by identifying optimal locations that receive maximum sunlight exposure throughout the day.

2. Weak Structural Design
Poorly designed structures can easily collapse under heavy loads and extreme weather conditions. Utilizing well-engineered frameworks ensures long-term durability and stability, providing reliable support for solar panels over time.
3. High Installation Costs
Although the initial cost of constructing solar structures can be relatively high, choosing cost-effective materials and innovative designs ensures long-term savings and a more sustainable investment in renewable energy solutions.
